Psoriasis is a disease that affects, according to WHO experts, from 2 to 4% of the world's population. A feature of the disease is that only representatives of the white race suffer from psoriasis. Determining the causes and treating psoriasis is considered one of the priority tasks of modern medicine. Today science has advanced a lot in these matters, but the causes of the disease have not yet been fully understood, just as no way has been found for a complete cure for this disease.

Causes of psoriasis
Physiologically, psoriasis is caused by an extremely short life cycle of skin cells. If normally this cycle is from 21 to 28 days, then in patients with psoriasis the cycle lasts only 3-6 days. This is what causes the formation of psoriatic plaques. The reason for this phenomenon is mainly debated among specialists. While some consider psoriasis to be a disease caused by hereditary factors, others believe that the disease manifests itself as a result of malfunctions in the immune system, which are a direct consequence of a whole host of different external factors.
Today, among doctors, the multifactorial theory prevails, which explains the occurrence of psoriasis for the following reasons:
- Inheritance;
- Immune system dysfunction due to:
- Delayed infectious diseases;
- Improper nutrition;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Unfavorable climatic conditions.

However, absolutely all experts agree on one thing, psoriasis is not a contagious disease and it is impossible to "catch" it on the street like the flu or sore throat.
Symptoms of psoriasis
Today, doctors consider psoriasis a systemic pathology, that is, it is customary to talk about psoriasis as a pathology with complex effects.
It is believed that the first signs of developing psoriasis are:
- A persistent feeling of general weakness;
- Feeling tired;
- Depression and frequent depression.
These symptoms should be alarming. However, the clinical symptoms of psoriasis are manifested in skin lesions. In the case of psoriasis, it is most often psoriatic plaques that appear suddenly on the patient's body. Initially, they may be small (a few millimeters), but over time they can grow significantly (up to 10 centimeters in diameter).
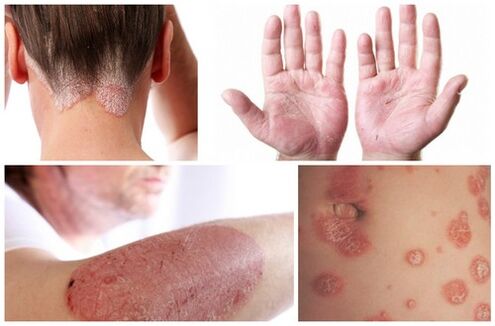
By the nature of the rash, psoriasis is usually divided into:
- Spot (plate diameter is small, does not exceed the diameter of a match head);
- In the form of dots, in the size of a lentil grain, but in the form of dots;
- Round coin-shaped plates, reminiscent of a coin up to 5 millimeters in diameter.
A feature of psoriasis is the formation of scales on the plaques, which are very easily removed. This is due to the fact that they are formed by keratinized epidermal cells. The scale forms initially in the center of the plate, and later spreads to the edges. Sometimes a pink ring forms around the plate, which indicates the growth of the plate itself. When the scales are removed, a shiny smooth surface of the skin remains, which has a pink color, due to the proximity of the location of the blood vessels (capillaries).
Classification of psoriasis, what does psoriasis look like (photo)
In most cases, doctors deal with common (vulgar) psoriasis. However, in about 10% of cases, the manifestations of psoriasis have other external signs, which can be clearly seen in the picture.
According to the external manifestations of psoriasis, it is customary to distinguish the following forms:
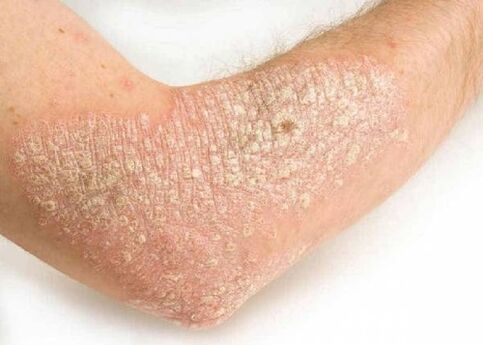
- Vulgar psoriasis (common). It starts with a rash of small papules ranging in size from a matchstick to a pea. Scaling occurs in these papules and the papule turns into a typical psoriatic plaque. As a rule, plates have well-defined borders, allowing them to be clearly visualized in relation to healthy skin. The plaque may itch. If the patient tries to remove a papule or plaque, desquamation is observed. Once the flakes are removed, a smooth, glossy surface appears. If you continue the itching process, blood droplets appear very quickly, the so-called "blood dew";
- Psoriatic erythroderma. This, an extremely unpleasant disease like a form of psoriasis, occurs in about 2% of those suffering from this disease. Erythroderma manifests itself in the form of severe itching, diffuse redness of the skin, as well as lamellar skin. Often, psoriatic erythroderma is associated with generalized pustular psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Often, infections such as streptococcal infections complicate the course of the disease. Sometimes erythroderma manifests itself spontaneously already in the first stage of psoriasis. In some cases, erythroderma develops as a result of improper treatment of psoriasis;
- Pustular psoriasis. This form of the disease is characterized by the formation of pustules that resemble small abscesses. With the flow, this form of psoriasis can be generalized and localized. With a localized form, pustules are located in the area of the feet and palms. With a generalized form, the patient has an increase in body temperature and signs of body intoxication. This form of psoriasis is very dangerous and can even be fatal;
- Psoriatic arthritis. Many experts distinguish it as an independent autoimmune disease. Appears in the form of an inflammatory process in the patient's joints and muscles;
- Psoriasis of the nail plates. In some cases, common psoriasis affects the nail plates, and then they talk about nail psoriasis. Loss of nail plates from psoriasis is very similar to a fungal infection. As a result of the disease, the nail plate can deform and even disappear completely in the end.
Treatment of psoriasis
Modern medicine does not yet have in its arsenal of tools capable of completely curing psoriasis; there is still not enough knowledge about the causes and characteristics of the course of the disease. However, in the arsenal of doctors there are a number of medications that can significantly alleviate the manifestations of psoriasis and transfer it from the acute phase to long-term remission. When treating psoriasis, the doctor takes into account the age, gender, lifestyle, health condition of the patient and only taking into account all these factors chooses a treatment strategy.
Very often, treatment of psoriasis begins with external therapy. This includes:

- Salicylic ointment, which is used when the disease progresses;
- Hormonal medications prescribed if salicylic oil is useless;
- Creams containing ditronal. They have anti-inflammatory effects and help eliminate the symptoms of psoriasis quite quickly.
But not always the means of external therapy bring the desired result. Then another treatment tactic is chosen and a systematic approach is considered one of the most effective methods today.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of psoriasis
There are a large number of traditional medicine prescriptions for psoriasis. Many of them really help in treating this disease. But do not overestimate the possibilities of such prescriptions, as traditional medicine can be used as an adjunct therapy, but in no case as a means of primary treatment.
Probably the most common traditional remedy for psoriasis is celandine. Unfortunately, this method can only be treated in the summer, when it is not a problem to find celandine. The essence of the method lies in the action of plant juice on the plates. It is enough to simply break the stalk and direct the drops of fluid in this fracture to the skin affected by psoriasis. This should be done daily for three months. It is believed that the maximum effect of treatment occurs in the third year of treatment.

In second place in popularity is birch tar, which is simply spread on the affected surface for an hour. According to another method, after such application of tar, it is recommended to use celandine juice. The course of treatment in the first case and in the second case is 15 days.
Egg-based ointment is considered very popular in the treatment of psoriasis. To prepare, take two raw eggs and mix them with sunflower (olive) oil and beat. After that, add half a tablespoon of vinegar to the resulting mixture. The affected areas are smeared with a mixture once a day. The mixture itself is stored in a dark, cool place.
Helps very well with the exacerbation of psoriasis and a bath to which is added a decoction of walnut shells. For a bath, you need to create shells from half a kilo of nuts. The bath is taken no more than 15-20 minutes at a temperature no higher than 37 degrees. It is recommended to take ten baths on vacation in one day.
Diet for psoriasis
According to many experts, proper nutrition in psoriasis is extremely important to avoid prolonged periods of disease exacerbation. It is believed that the essence of the diet is to maintain acid-base balance to the alkaline component. So 70-80% of the products should be alkaline and only 20-25 acid-forming.
Those that form alkali include:
- Fruit (except black and red cranberries, prunes, plums and grapes);
- Vegetables (excluding legumes, Brussels sprouts, squash, potatoes, tomatoes, peppers and eggplants).

It is common to refer to products that form acid:
- Starch;
- Cheese;
- Sugar;
- meat
- Butter;
- Cream.
Thus, the diet of a patient with psoriasis should include:
- water (at least 2 liters per day);
- Fresh fruit, steamed (canned fruit not desirable). Apples, dates, figs, apricots, oranges, peaches, raisins are recommended;
- Vegetables, also fresh or steamed. Recommended beets, cucumbers, lettuce, carrots, celery, spinach, zucchini, watermelon, cabbage.
- Cereals (in small quantities). Buckwheat porridge, wheat, barley, millet, as well as baked foods with rice and corn flour are recommended;
- Low fat fish, four times a week;
- Poultry (chicken), two to three times a week. It is permissible to give a sick young sheep once a week;
- Milk (skimmed is best);
- Soft-boiled eggs, two to three times a week;
- Vegetable oil in the amount of 3 teaspoons per day.

Prophylaxis
And although there is no way to prevent psoriasis, there are ways to significantly reduce its manifestations and maximize the remission phase.
For this you need:
- Take care of your skin and keep it moist;
- Excessive exposure to cold or hot air should be avoided;
- Minimize the possibility of damage to the skin surface;
- Give up alcohol and tobacco;
- All diseases are from the nerves, so you need to minimize the stressful effects and try to be in harmony with yourself and the world around you.























